Power and Energy Systems
The centre is a world reference in large-scale integration of Distributed Energy Resources. Our expertise led us to take on key roles in important EU projects and also led to contracts for development and consultancy with manufacturing equipment companies and with power generation, transmission and distribution companies, regulators, government agencies and investors in Europe, South America, the United States of America and Africa.
At CPES, we address the following main research areas: Decision Making, Optimisation and Computational Intelligence, Forecasting, Static and Dynamic analysis of Energy Grids, Reliability, Power Electronics.
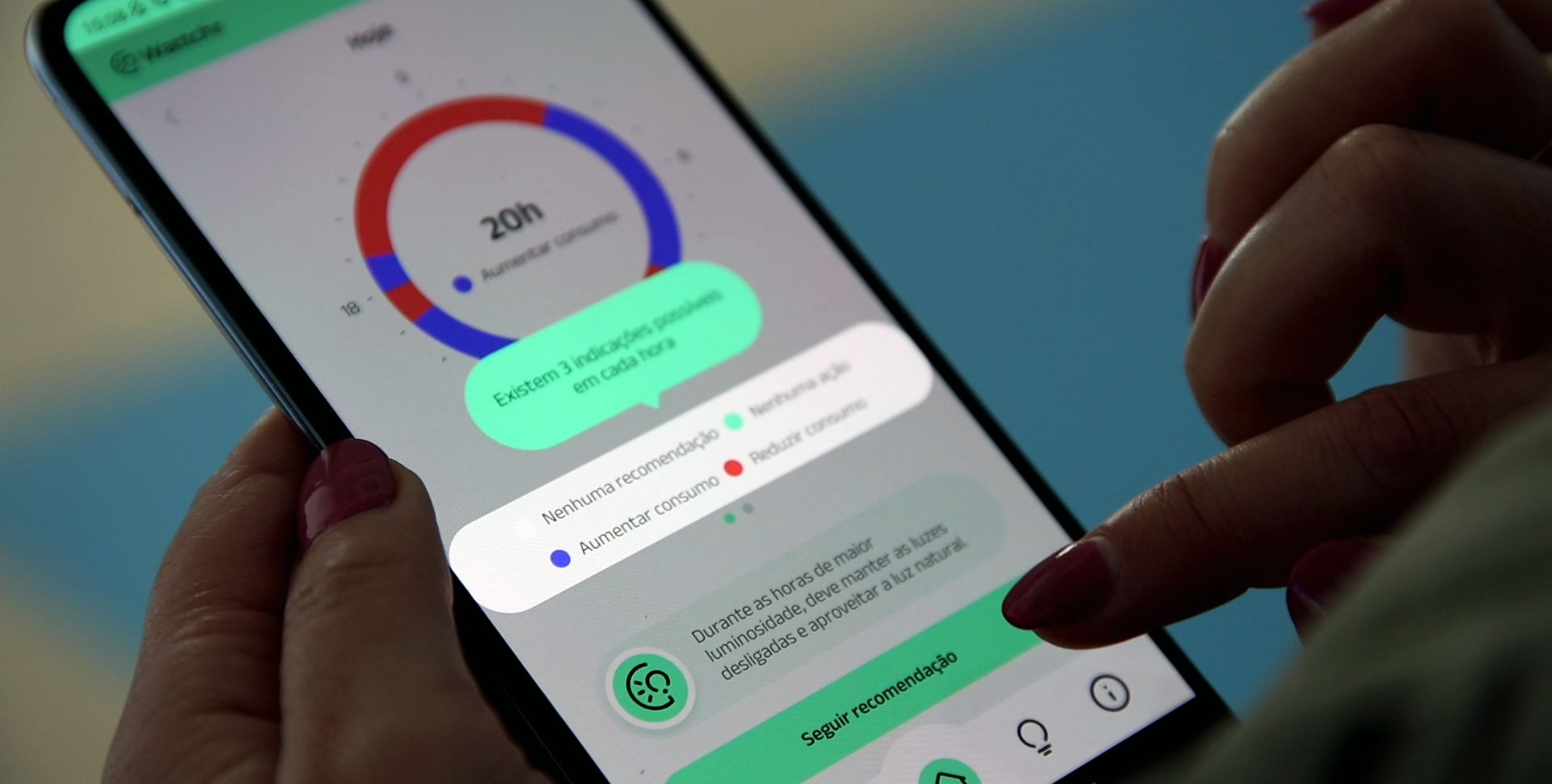
Part of our activity is developed in the Laboratory of Smart Grids and Electric Vehicles that supports the validation of major developments in a real environment.
Over the last years, we have made several developments in the electrical network planning and operation, namely the inclusion of distributed energy resources forecasting and network optimisation tools embedded in different voltage layers, exploiting the MicroGrid hierarchical concept. Relevant steps were given on the inclusion of computational intelligence in control algorithms that were demonstrated under real conditions in several pilots.