Centro de Sistemas de Energia
O centro é uma referência mundial na integração em larga escala de recursos distribuídos. As suas competências levaram à atribuição de papéis decisivos em projetos importantes da UE, assim como deram origem a contratos de desenvolvimento e consultadoria com empresas fabricantes de equipamentos e com empresas de geração, transmissão e distribuição de energia, autoridades reguladores, agências governamentais e investidores na Europa, América do Sul, Estados Unidos da América e África.
O CPES aborda as seguintes áreas principais de investigação: Tomada de Decisão, Otimização e Inteligência Computacional, Previsão, Análise Estática e Dinâmica de Redes de Energia, Confiabilidade, Eletrónica de Potência.
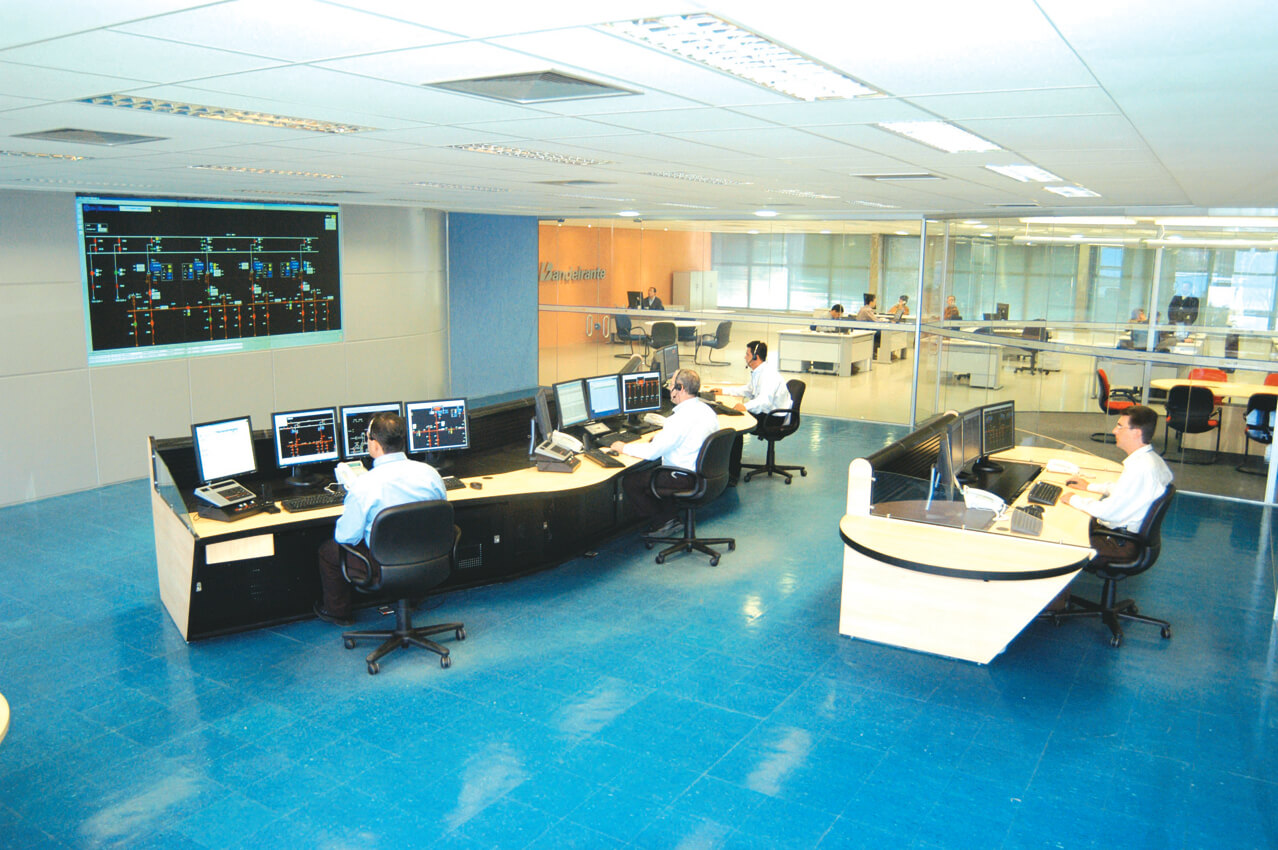
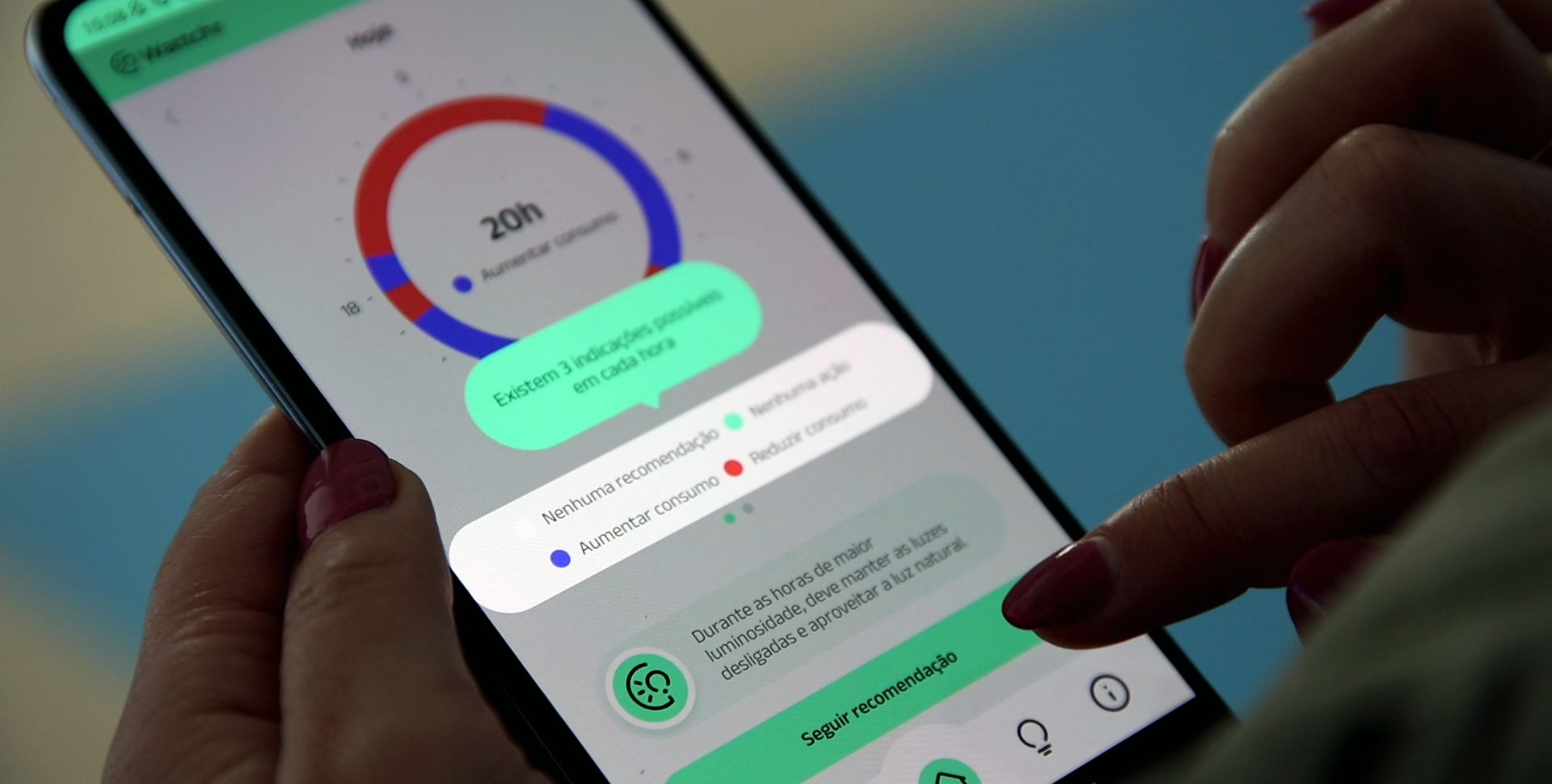
Uma parte do trabalho do CPES é desenvolvido no Laboratório de Redes Elétricas Inteligentes e Veículos Elétricos, que apoia a validação de importantes desenvolvimentos num contexto real.
Nos últimos anos, foram desenvolvidas várias iniciativas no planeamento e operação da rede elétrica, nomeadamente a integração da previsão dos recursos distribuídos e das ferramentas de otimização da rede que são incorporadas em diferentes camadas de tensão, explorando o conceito hierárquico de MicroGrid. Foram tomadas as iniciativas necessárias para a integração da inteligência computacional em algoritmos de controlo, comprovados em situações reais por vários projetos-piloto.