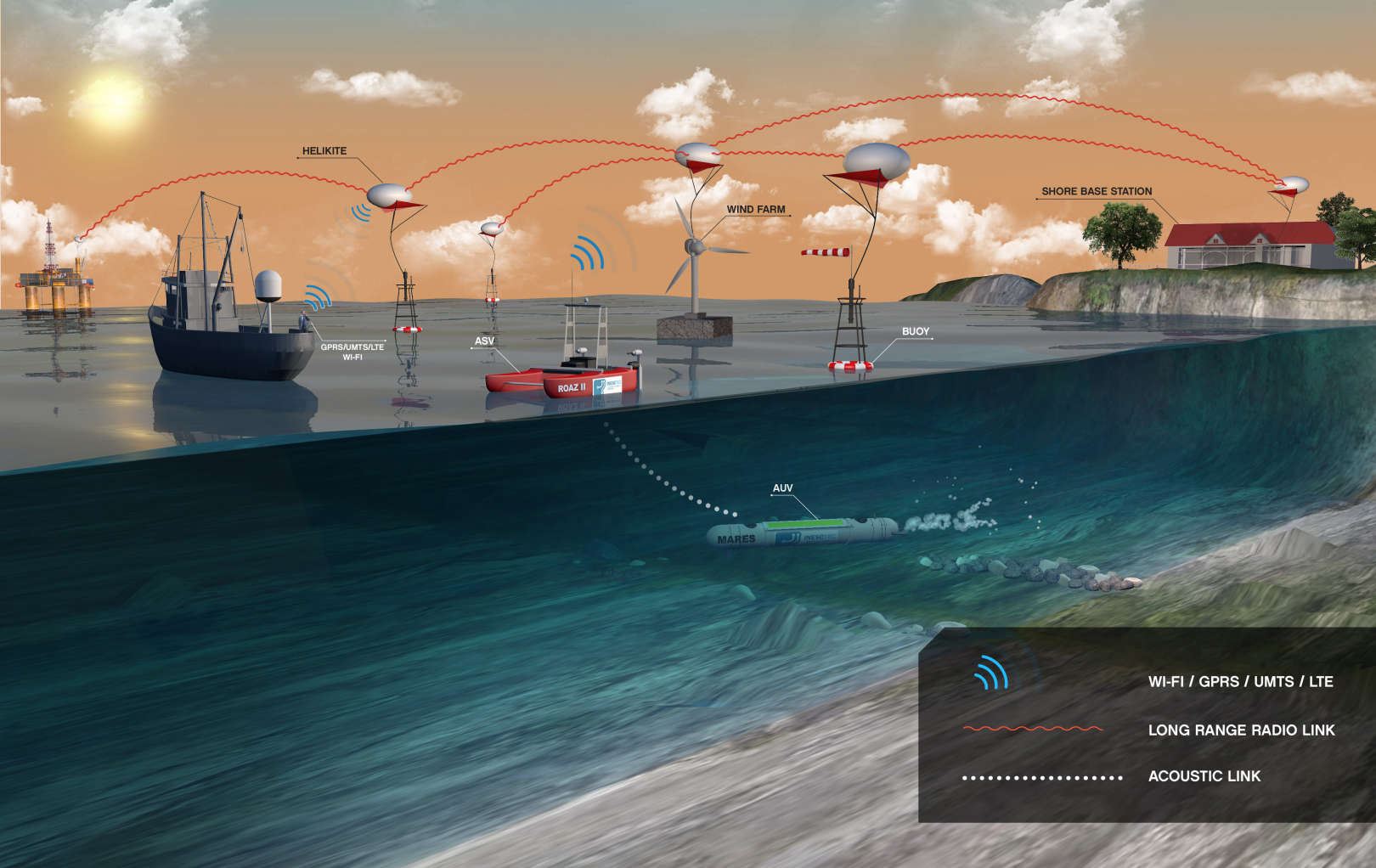
Sobre
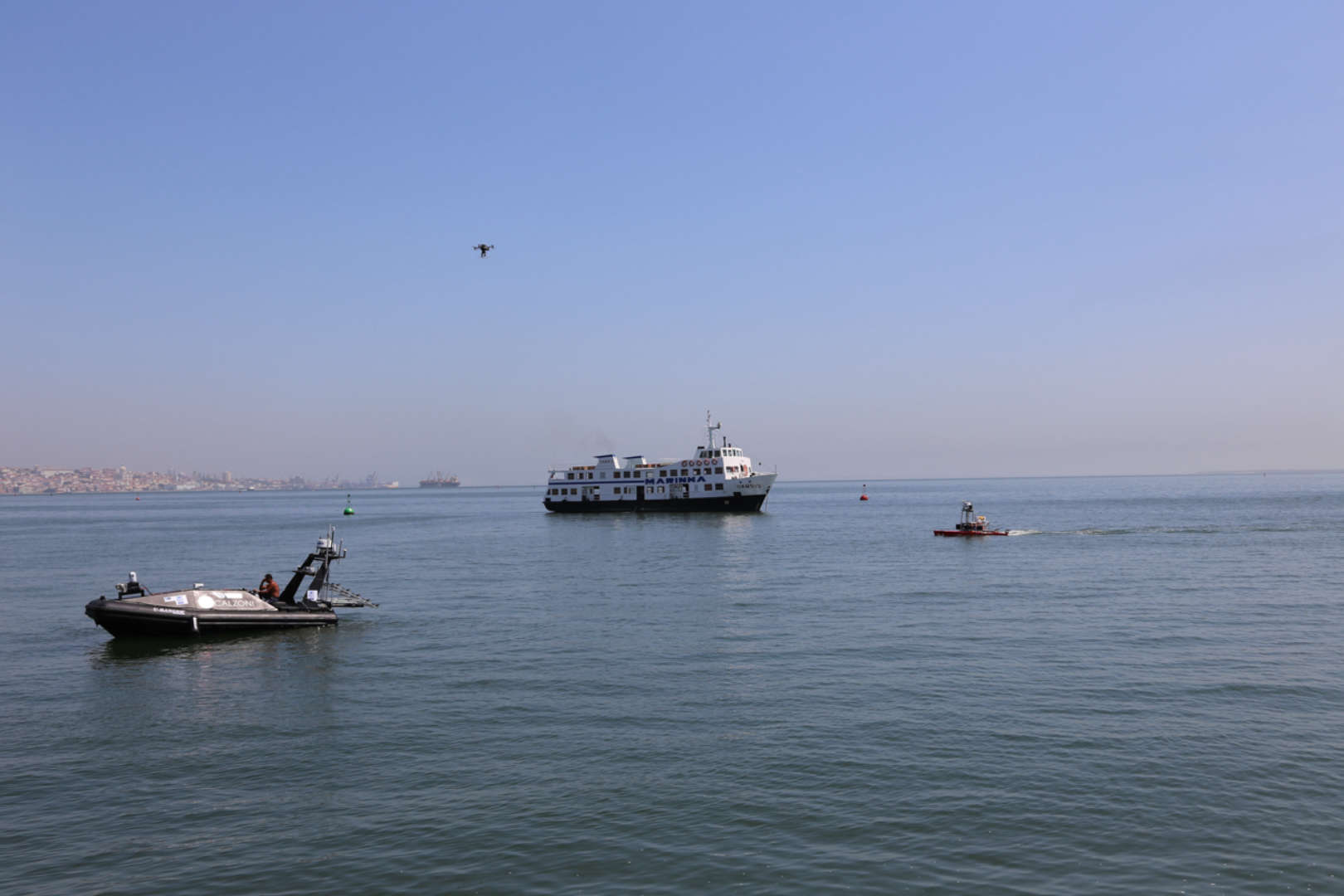
Sou investigador sénior no Centro de Telecomunicações e Multimédia do INESC TEC, e coordenador da área de tecnologia ótica e eletrónica. Concluí a licenciatura em 2006 e o doutoramento em 2011, ambos em Engenharia Electrotécnica e de Computadores, pela Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto. Atualmente sou responsável pela conceção e gestão de projetos de I&D, orientação de alunos de mestrado/doutoramento e bolseiros de investigação, e por promover a valorização de resultados de investigação através de novos contratos com a indústria. Estive envolvido como professor assistente convidado da Universidade do Porto nas disciplinas de engenharia de rádio e microondas e comunicações óticas. Sou autor/co-autor de mais de 50 publicações em conferências e revistas internacionais com revisão por pares, e de uma patente europeia. Já coordenei vários projetos de investigação e participei em vários projetos europeus. Os meus principais interesses de investigação incluem sistemas óticos coerentes, rádio-sobre-fibra, dispositivos rádio/microondas e antennas, transferência de energia sem fios e comunicações subaquáticas.